A monitoring plan is essential for long-term success. Unfortunately, many costly structures have been installed then fail because of inadequate monitoring and maintenance.
A simple plan that ensures monitoring and adjustments as needed is preferred to a complex plan that is hard to implement. Each plan needs to include a schedule for site visits and actions to take when an issue is identified.
.

.
.
.
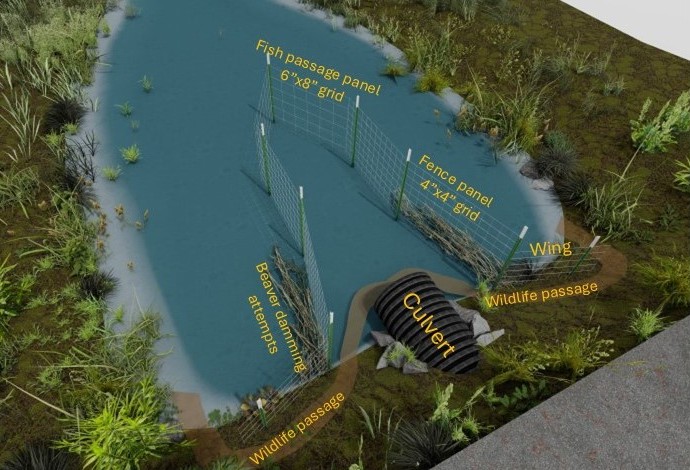
Culvert Version Example – Monitoring/Maintenance Plan
Monitoring Plan for ___________________
1 –Day one – After installation check the structure. The first few days are when problems are most likely to occur. Recheck the structure the next day, then every 2-3 days until the structure is functioning as intended and only minor damming efforts are occurring.
2- Follow-up inspection – When the structure is functioning properly for several days, schedule an additional site visit in 30 days to verify that the structure is still functioning as intended.
3- Annual inspection and maintenance – When the structure is functioning as intended for 30 days, schedule annual site visits in the fall, when beavers are most active. Conduct any maintenance that might be needed. Document issues identified and actions taken.
Maintenance Plan (examples of what could be included)
- Situation- Beavers have pushed tree limbs and debris through the 4”x4” fence panels. Branches and debris pushed against the outside of the fence panel is OK to leave. Limbs and sticks poked through the panel should be pruned, leaving 3”-5” within the lane as they will not interfere with water flow, and will prevent additional material being poked through.
- Situation- Beavers have tunneled under the fence panel and attempted to rebuild a dam at the culvert. Add a 2’x3’ section of 4”x4” or 6”x8” fence panel as a patch over the section of skirt that has been breached by a beaver.
- Situation – Beavers drag material around the wing and block the culvert. Place a temporary panel between the wing and the culvert to block beaver access to the culvert. Remove the panel after a month as beaver likely will give up on the site.
- Situation- Beaver access the site and utilize grass and mud within the lane fence to plug the culvert. Temporarily place a 6”x8” grid section of panel that is 6-10 feet long in the bottom of the lane fence to discourage digging within the lane fence.
- Situation- When all efforts fail. A well-established beaver colony can be persistent, which may require trapping and removal. After removal of an existing colony, the SBB device creates an unsuitable site for new beavers to start a dam.
- Situation- Fence is collapsing inward due to soft pond floor. Add a cross-tie connecting T-posts on opposite sides of lane.
